Your cart is currently empty!
What is DMAIC Methodology?
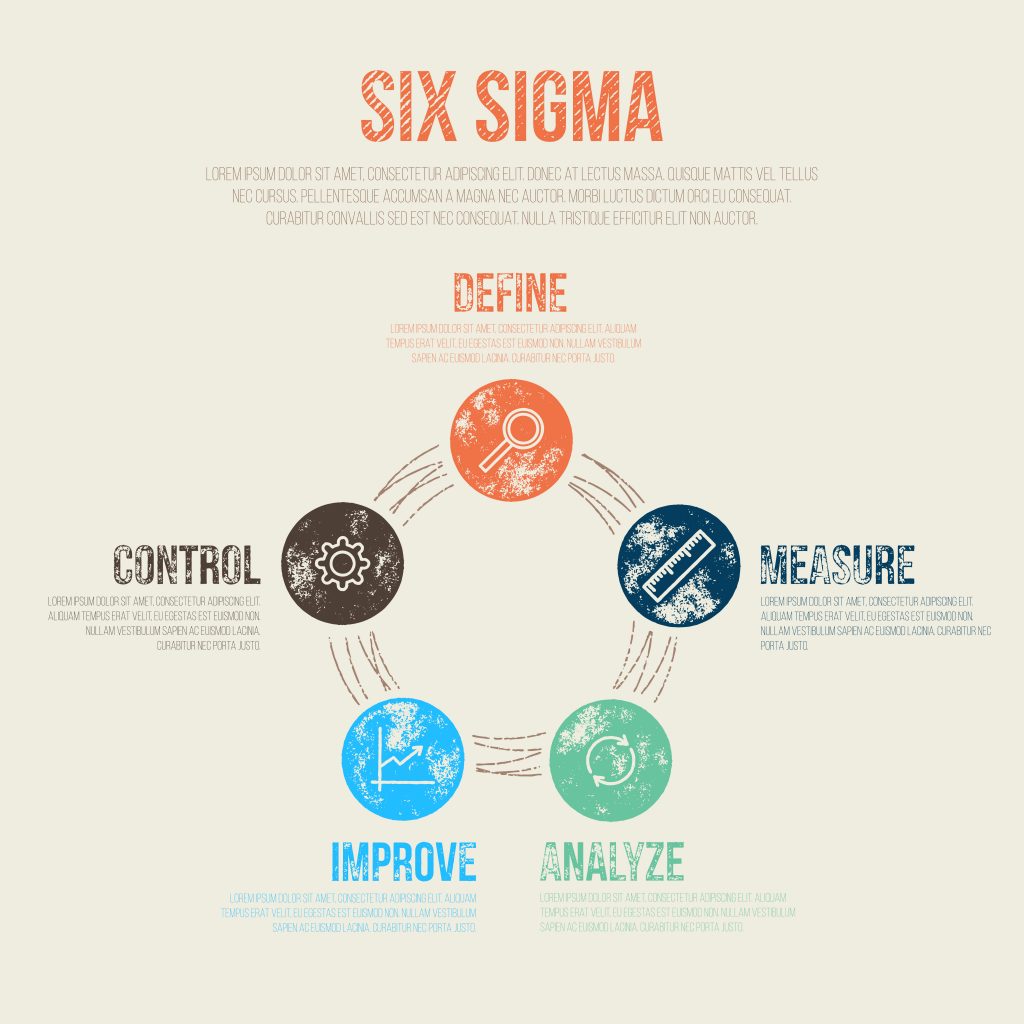
Six Sigma is a method used by companies to improve a process, resulting in a more streamlined process with less waste and a more consistent product with fewer defects. While Six Sigma is frequently associated with manufacturing plants, the system can be implemented successfully in a variety of organizations, such as business offices and service companies. Most organizations use DMAIC methodology to develop their Six Sigma programs. DMAIC is an acronym of the methodology’s five steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control.
- Define: In the Define step, the organization must define problems and goals, such as who are the customers, and what are their requirements? Which processes are targeted for improvement? What steps make up those processes? What are the quality issues?
- Measure: The next step is to measure the process that has been targeted for improvement. Come up with a data collection plan for the process and then collect the data. Perhaps you’re measuring how many products fall outside the customer’s parameters, how many times the production line is backed up, or in an office setting, how many project reports are turned in late.
- Analyze :After collecting the data, analyze it to find where the current performance is not meeting performance goals. Look for opportunities to improve the process – find the causes of defects, bottlenecks and spots where there is too much variation in the process.
- Improve: Design solutions to improve the process. Create a test plan and try out the different solutions to learn which ones best solve the identified problems without creating new problems.
- Control: Control the improvements to the process to keep it on course. Resist going back to the old way of doing things, and continue to monitor the process and take measurements regularly to ensure that the solutions are working.

Leave a Reply